Diffusion imaging of organs with small cross-sections like the prostate and spinal cord is frequently desired. In these cases the surrounding tissues may be of no interest and serve only to contribute noise and aliasing artifacts. Accordingly, so small field-of-view (FOV) methods have been developed to exclude these unwanted regions. These can be used not only for DWI but routine imaging as well.
|
Two of the oldest approaches to small FOV imaging derive from MR spectroscopy. Inner volume excitation uses either 2 or 3 perpendicularly applied RF-pulses to excite voxels only along their intersection (a column of voxels or single voxel respectively). Alternatively, outer volume suppression bands can be used to null signal from tissues outside the desired imaging volume.
|
A variant of inner volume excitation has recently been developed and now offered as product by the major vendors as FOCUS (GE), ZOOMit (Siemens), and iZOOM (Philips). These sequences employ a special 2D RF excitation pulse that is spatially selective in both the slice select and phase-encoding directions. It takes the place of the 1D slice-selective 90º-pulse used in conventional EPI sequences.
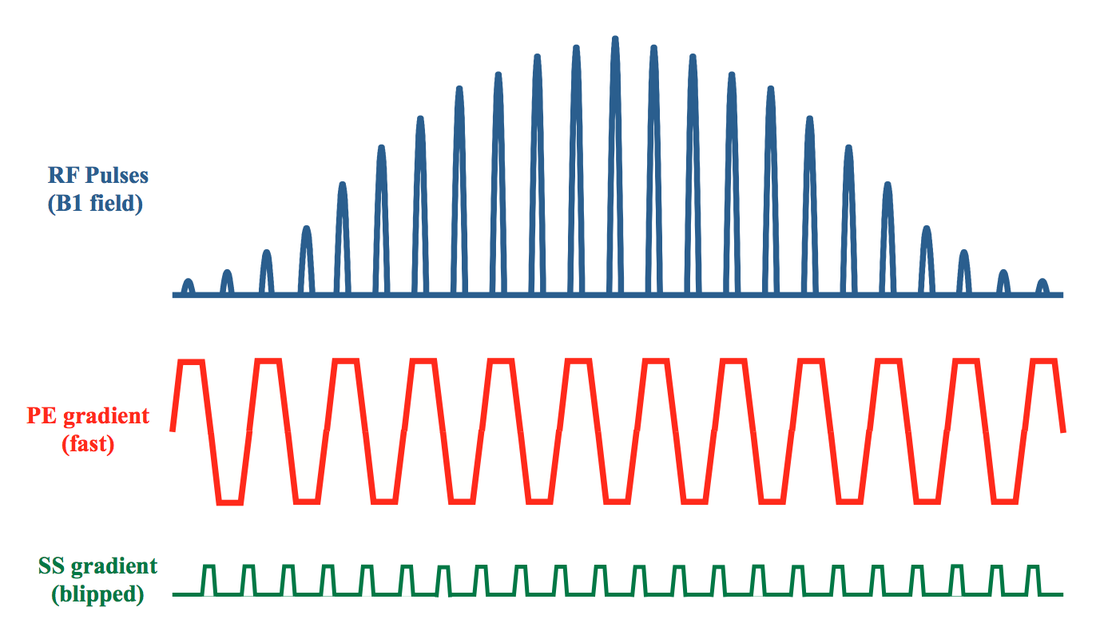
Details of a sample 2D RF-pulse used for a small FOV sequence are shown in the diagram below. The 2D RF "pulse" is a composite of approximately 25 closely spaced "sub-pulses" extending over a time frame of about 15 ms. This RF excitation is played out simultaneously with a fast (oscillatory) gradient along the phase-encode axis and a slow ("blipped") gradient along slice-select.
Slice thickness in both phase- and slice-select directions can be independently controlled. Orienting the fast gradient along the phase-encode axis allows for a very sharp profile and minimizes aliasing. The slow ("blipped") gradient has a much lower bandwidth, and orienting it along the slice-select axis means that fat-water chemical shift displacements will occur in this direction. By choosing the main lobe of water to be on-resonance during refocusing, "fat ghosting" artifacts common in EPI can be largely eliminated. A 3-mm-thick prostate DW image using small FOV technique is shown below right.
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
No supplementary material yet. Check back soon!
References
Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ. Two-dimensional spatially selective spin inversion and spin-echo refocusing with a single nuclear magnetic resonance pulse. J Appl Phys 1987; 62:4284-4290. (Original description of 2D RF pulses.)
Feinberg DA, Hoenninger JC, Crooks LE, et al. Inner volume MR imaging: technical concepts and their application. Radiology. 1985;156:743–747. (early method using intersection of two perpendicularly excited slabs to limit imaged volume)
Frahm J, Merboldt K-D, Hänicke W. Localized proton spectroscopy using stimulated echoes. J Magn Reson 1987; 72:502-508. (the STEAM technique, commonly used in MR spectroscopy to excite a single voxel using three perpendicular excitation pulses)
Ma C, Xu D, King KF, Liang Z-P. Reduced field-of-view excitation using second-order gradients and spatial-spectral radiofrequency pulses. Magn Reson Med 2013; 69:503-508.
Pauly J, Speilman D, Macovski A. Echo-planar spin echo and inversion pulses. Magn Reson Med 1993; 29:776-782.
Saritas EU, Cunningham CH, Lee JH, Han ET, Nishimura DG. DWI of the spinal cord with reduced FOV single-shot EPI. Magn Reson Med 2008; 60:468-473.
Wilm BJ, Svensson J, Henning A, et al. Reduced field-of-view MRI using outer volume suppression for spinal cord diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 2007; 57: 625–630.
Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ. Two-dimensional spatially selective spin inversion and spin-echo refocusing with a single nuclear magnetic resonance pulse. J Appl Phys 1987; 62:4284-4290. (Original description of 2D RF pulses.)
Feinberg DA, Hoenninger JC, Crooks LE, et al. Inner volume MR imaging: technical concepts and their application. Radiology. 1985;156:743–747. (early method using intersection of two perpendicularly excited slabs to limit imaged volume)
Frahm J, Merboldt K-D, Hänicke W. Localized proton spectroscopy using stimulated echoes. J Magn Reson 1987; 72:502-508. (the STEAM technique, commonly used in MR spectroscopy to excite a single voxel using three perpendicular excitation pulses)
Ma C, Xu D, King KF, Liang Z-P. Reduced field-of-view excitation using second-order gradients and spatial-spectral radiofrequency pulses. Magn Reson Med 2013; 69:503-508.
Pauly J, Speilman D, Macovski A. Echo-planar spin echo and inversion pulses. Magn Reson Med 1993; 29:776-782.
Saritas EU, Cunningham CH, Lee JH, Han ET, Nishimura DG. DWI of the spinal cord with reduced FOV single-shot EPI. Magn Reson Med 2008; 60:468-473.
Wilm BJ, Svensson J, Henning A, et al. Reduced field-of-view MRI using outer volume suppression for spinal cord diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 2007; 57: 625–630.